A geogrid retaining wall is a reliable solution used to support soil and control ground movement in many construction projects. It helps builders manage slopes, uneven land, and heavy loads with better stability. By using geogrid reinforcement, the soil becomes stronger and more resistant to pressure. This method supports retaining wall reinforcement without relying only on concrete. Many engineers choose this approach because it improves soil stabilization systems and increases safety. A geogrid retaining wall also adapts well to natural ground movement, which reduces cracking over time. From residential landscaping to large infrastructure work, this system plays an important role in modern earth retention systems and long-term structural soil support.
What Is a Geogrid Retaining Wall?
A geogrid retaining wall uses polymer grids placed between soil layers to increase strength. These grids interlock with soil, creating reinforced earth structures. This method improves load distribution and reduces pressure on wall faces.
In construction, retaining wall reinforcement using geogrids supports taller walls safely. This approach forms part of modern earth retention systems, making it ideal for projects requiring stability without bulky concrete structures.
How a Geogrid Retaining Wall Works
Understanding how this reinforced wall system works begins with soil interaction. The geogrid layers lock into compacted soil and spread forces outward rather than downward. This process reduces wall movement and minimizes the risk of soil failure.
As part of reinforced soil walls, the system balances tension and friction within the soil mass. This interaction provides strong structural soil support that performs well even under heavy loads or challenging ground conditions.
Benefits of Using a Geogrid Retaining Wall
The main benefits of geogrid retaining walls include strength, flexibility, and cost efficiency. Unlike rigid concrete structures, they adjust to minor ground movement without cracking. This flexibility improves overall durability.
By improving soil stabilization systems, this construction method extends service life and lowers long-term maintenance needs. Engineers prefer it for projects that demand reliable and sustainable ground reinforcement.
Common Applications of a Geogrid Retaining Wall
A geogrid retaining wall for slope support is commonly used along highways, residential landscapes, and uneven building sites. These structures help prevent erosion while maintaining natural land contours.
They are also widely used in parking areas and commercial developments. With proper geogrid reinforcement, builders achieve stable results even on weak or variable soil.
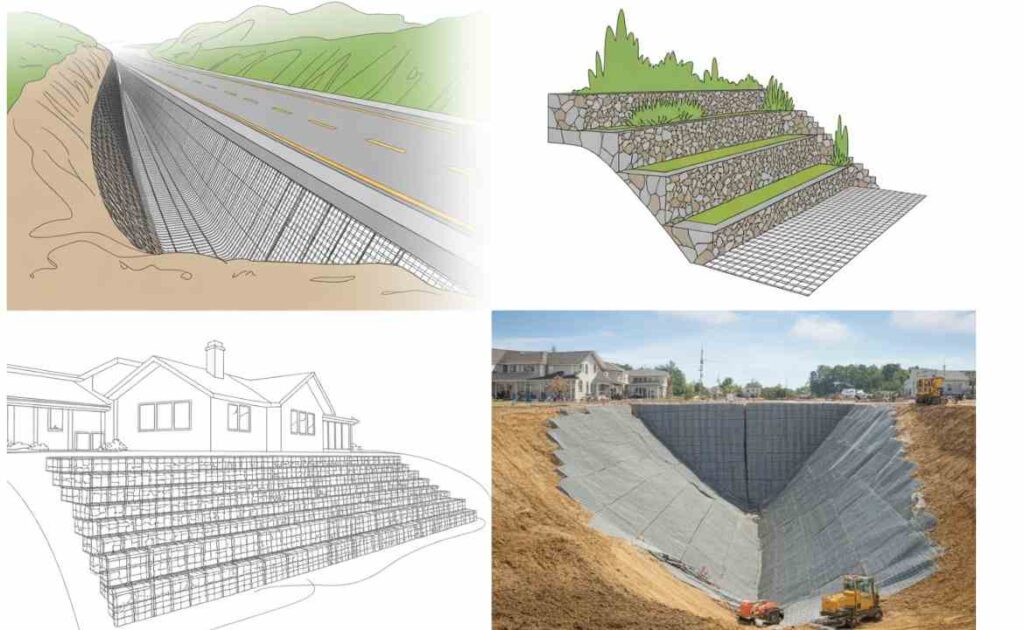
Types of Geogrid Used in Retaining Walls
Manufacturers produce uniaxial and biaxial geogrids to handle different load directions. Each type supports specific slope stabilization and soil conditions depending on project needs.
Selecting the correct grid type improves reinforced soil wall performance. Engineers carefully match grid strength with wall height and soil characteristics to ensure safety and longevity.
Installation Process of a Geogrid Retaining Wall
Installing a geogrid retaining wall requires careful base preparation and proper soil compaction. Workers place geogrid layers horizontally between soil lifts to create a strong interlocking system.
Correct spacing and alignment ensure the geogrid reinforcement works effectively. When installed properly, the wall remains stable and resists pressure for many years.
Cost and Longevity of a Geogrid Retaining Wall
A geogrid retaining wall often costs less than concrete alternatives. Reduced material needs and faster installation save labor expenses.
The long-term performance of geogrid walls is impressive. With proper design, these systems last for decades with minimal maintenance.
| Factor | Impact |
| Installation Speed | Faster than concrete walls |
| Maintenance | Low |
| Lifespan | 50+ years |
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Geogrid Retaining Walls
Ignoring soil testing weakens retaining wall reinforcement and increases the risk of failure. Poor drainage design can also cause long-term performance issues.
Another common mistake is insufficient grid overlap, which reduces structural soil support. Proper planning ensures the system performs as intended throughout its lifespan.
Future Trends in Geogrid Retaining Wall Construction
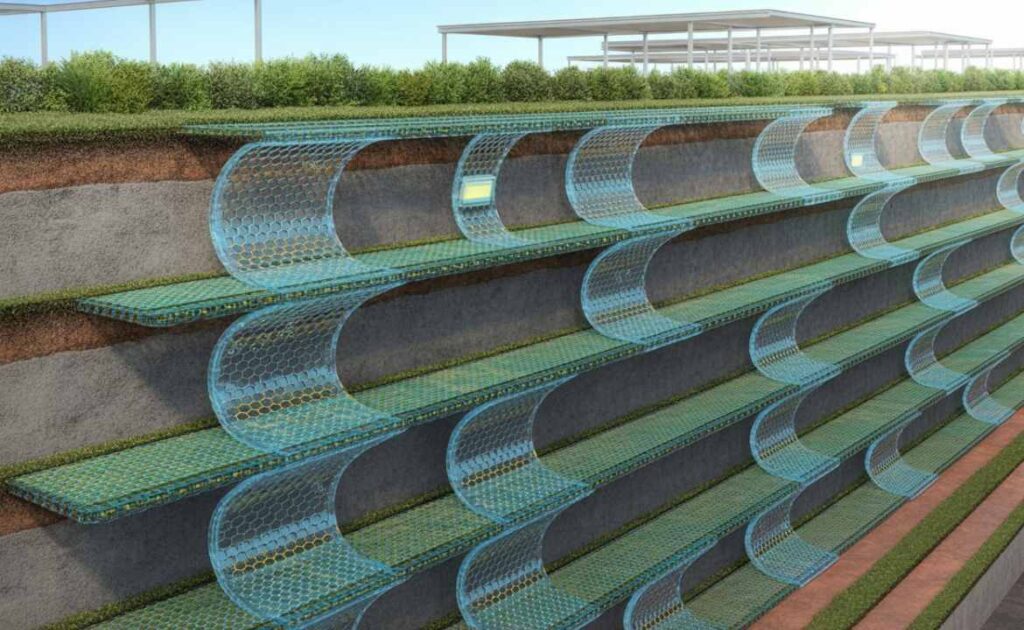

New materials continue to improve soil stabilization systems. Advanced polymers now offer higher durability and better resistance to environmental stress.
Sustainable construction practices favor geogrid-based retaining solutions for their efficiency and lower material use. Expect smarter designs and wider adoption in future infrastructure projects.

